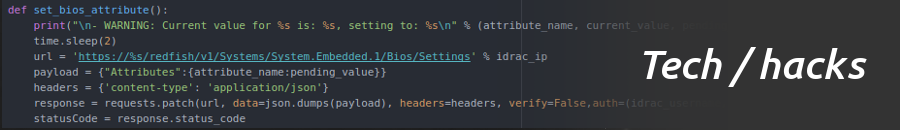
Pull current settings:
C:\Users\Administrator>racadm -r 10.6.26.241 -u root -p calvin get BIOS.BiosBootSettings.HddSeq
[Key=BIOS.Setup.1-1#BiosBootSettings]
HddSeq=RAID.Integrated.1-1,Disk.SDInternal.1-1
Update boot order:
C:\Users\Administrator>racadm -r 10.6.26.241 -u root -p calvin set BIOS.BiosBootSettings.HddSeq Disk.SDInternal.1-1,RAID.Integrated.1-1
[Key=BIOS.Setup.1-1#BiosBootSettings]
RAC1017: Successfully modified the object value and the change is in
pending state.
To apply modified value, create a configuration job and reboot
the system. To create the commit and reboot jobs, use “jobqueue”
command. For more information about the “jobqueue” command, see RACADM
help.
Verify setting is in PENDING state:
C:\Users\Administrator>racadm -r 10.6.26.241 -u root -p calvin get BIOS.BiosBootSettings.HDDSeq
[Key=BIOS.Setup.1-1#BiosBootSettings]
HddSeq=RAID.Integrated.1-1,Disk.SDInternal.1-1
(Pending Value=Disk.SDInternal.1-1,RAID.Integrated.1-1)
Create job!
C:\Users\Administrator>racadm -r 10.6.26.241 -u root -p calvin jobqueue create BIOS.Setup.1-1
RAC1024: Successfully scheduled a job.
Verify the job status using “racadm jobqueue view -i JID_xxxxx” command.
Commit JID = JID_995403790233
Reset machine to get Lifecycle Controller to execute change:
C:\Users\Administrator>racadm -r 10.6.26.241 -u root -p calvin serveraction hardreset